Get Free Consultation!
We are ready to answer right now! Sign up for a free consultation.
I consent to the processing of personal data and agree with the user agreement and privacy policy
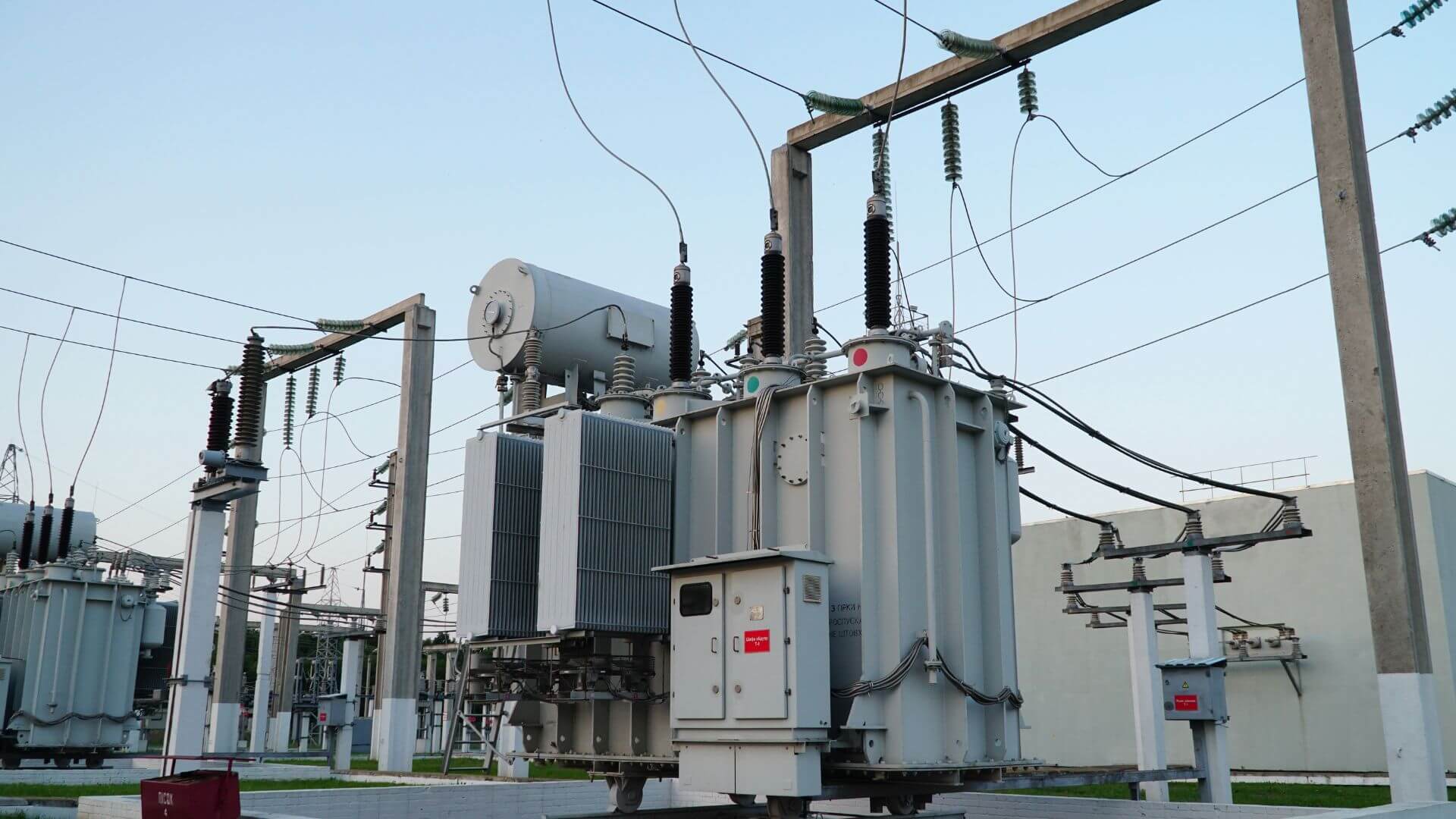

A power transformer is an electrical device used to transfer electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. Transformers are essential for adjusting the voltage levels in the electricity grid, making it suitable for safe consumption in homes and industries.
Power transformers typically operate at high voltages (greater than 33 kV) and are used in power generation stations, substations, and large-scale industrial applications. These transformers can either step up (increase) or step down (decrease) the voltage of electricity depending on where it is in the grid.
Power transformers rely on the principle of electromagnetic induction to transfer energy. Here’s a simplified explanation of how they work:
AC Voltage is Applied: An alternating current (AC) passes through the primary coil (input side) of the transformer, creating a magnetic field around it.
Magnetic Field: The magnetic field from the primary coil induces a current in the secondary coil (output side) without direct electrical contact. This is the key to transferring electricity between the two coils.
Voltage Change: Depending on the ratio of turns between the primary and secondary coils, the voltage is either stepped up or stepped down.
Step-up Transformer: The secondary coil has more turns than the primary coil, which increases the voltage.
Step-down Transformer: The secondary coil has fewer turns than the primary coil, which reduces the voltage.
The result is the safe delivery of electricity at the appropriate voltage for use, whether it's for high-voltage transmission or low-voltage household consumption.
There are several types of power transformers, each designed for different applications and voltage ranges. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
Step-Up Transformers:
Purpose: Increases voltage from low to high.
Application: Used in power plants to increase the voltage before it travels long distances through the transmission lines.
Step-Down Transformers:
Purpose: Reduces high voltage to a safer, usable level.
Application: These are the transformers that step down high-voltage transmission to the 110V or 220V commonly used in homes and businesses.
Distribution Transformers:
Purpose: Distributes electricity to homes, businesses, and industries at lower voltages.
Application: These transformers are typically found on utility poles or in substations near residential and commercial areas.
Isolation Transformers:
Purpose: Isolates electrical circuits to prevent the transfer of faults.
Application: Used in sensitive equipment like medical devices or for safety reasons in various industries.
Autotransformers:
Purpose: Uses a single coil to serve as both the primary and secondary windings, offering a more compact and cost-effective design.
Application: Used when only a slight voltage change is needed.
We will answer any questions you may have about our online sales.
We are ready to answer right now! Sign up for a free consultation.
I consent to the processing of personal data and agree with the user agreement and privacy policy
